Interaction between Indonesian Society with the new Hindu-Buddhist tradition Part #1
Prambanan Temple

Introduction
After we knew about History of The emergence and growth of Hindu-Buddha Religion and Hindu-Buddha Culture in Indonesia, now it is time for use to understand how that new Culture interact with Indonesian People. We see those interaction in many different aspect.
The entry of a foreign culture into the sphere of a society can lead to three possibilities: the two cultures will acculturated, move away from each other, or one of them destroyed. Acculturation is the cultural mixing of two or more cultures into a new culture. In the development of trade relations between India, China, and Indonesia, acculturation happened. Acculturation Hindu-Buddhist India with the indigenous cultures of Indonesia in a peaceful way created a new culture called the Hindu-Buddhist culture of Indonesia.
Facing the acculturation process, according to experts, the Indonesian people is passive and active. At first they passive receive new teachings, later actively seek knowledge to send their students abroad and invited Brahmins from abroad to give lessons.
Acculturation process for centuries raises syncretism between the two religions and cultural elements of the original, and from this a new religion was born, the religion knows as Shiva Buddha. Syncretism is a new concept or new -ism which is a blend of some concept or -ism to find harmony and balance. This stream is growing rapidly in the 13th century AD. The follower / supporter of Syncretism, among others is King Kertanegara ( Singhasari Kingdom ) and Adityawarman ( king of Malayapura, Cousin of Jayanegara King of Majapahit ).
Acculturation most easily be seen in the form of art, such as fine arts, literary arts, and the art of building which a part of material culture. This acculturation also could be witnessed in ritual ceremonies. Implementation of the acculturation process performed by scholars, theologians, architects, writers, people of the palace and the artists.
Below, is the list of aspect that we will cover that showing how Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences Indonesian People.
- Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on the building art
- Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on art
- Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on literary arts
- Hindu-Buddhist cultural influence on government system
- Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on belief systems
- Trade and transportation system
- Land tenure systems
- Tax system
- Labor
- Development of Hindu-Buddhist tradition
Since it will take a lot of time to cover all of this, i will split this article into two. This first article will cover the point 1 to point 5.
1. Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on the building art
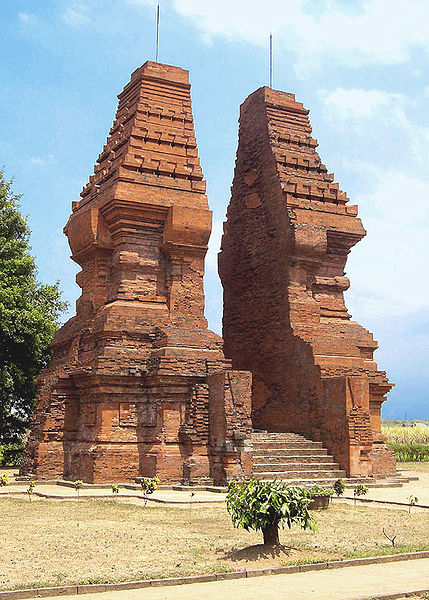
Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences in architecture or art building can we see clearly in the temples building in Indonesia. There is a difference between the functions of the temple in the Hindu and the Buddhist temple ( Temple was called Candi in Indonesia ). In Hinduism, the temple functioned as a tomb. As in Buddhism, the temple serves as a place to worship God.
Although Hindu Temples used as a tomb, but it does not mean that the bodies or ashes buried in the temple. Objects that buried are some objects that called pripih. Pripih is considered a symbol of bodily substances whose spirits are united with the god. Pripih was placed in a stone coffin at the base of the building, and a statue of the god made at it's top as a manifestation of the king. Statue of the king embodiment is generally is Shiva or Shiva symbol, the linga. In Buddhist temples, there are no pripih and statue of embodiment of the king. King's ashes planted around the temples in stupas building.
The building of the temple consists of three parts, the legs, body and roof.
- Temple Food is Square shaped. In the middle of the temple foot pripih is planted.
- The temple body consists of a chamber containing the statue of embodiment. The outer walls of the booth were given niche that contains a statue. South side wall niches containing statues of Guru, northern niches containing statues of Durga, and rear niches contain statues of Ganesha. Niches for large temples are usually changed.
- The roof of the temple consists of three levels.The top was smaller and there at its peak located a phallus or a stupa.The inside of the roof (top chamber) there is a small cavity is basically a rectangular stone with a picture of a red lotus, symbolizing the throne of god. In the worship ceremony, the bodies of the pripih have it's spirit raised from the cavity or lowered into the statue embodiment. The Statues than live and became the embodiment of the deceased as a god.
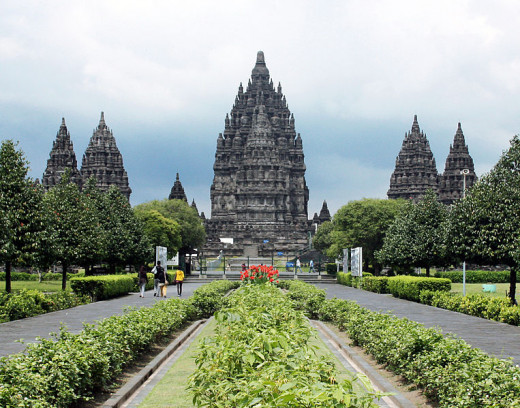
Building temples in Indonesia with Hindu styled, among others are, Prambanan temple, Sambisari temple, Ratu Boko temple, Gedongsongo temple, Sukuh temple, Dieng temple, Jago temple, Singasari temple, Kidal temple, Panataran temple, Surawana temple and archway Bajang Ratu.
Buddhist-style temple building, among others are, Borobudur temple, Mendut temples, Pawon temple, Kalasan temple, Sewu temple, Sari temple, and the Barelang temple.
Some relics of another building that resembles a temple as follows.
- Patirtan or bath, for example, patirtan in Jalatunda and Hemisphere (the slopes of Mount Indemnity), at the Tikus Temple (Trowulan), and at Gona Gajah (Gianyar, Bali).
- Padas Temple in Kawi Mountain, Tampaksiring. In this place there are ten temples were carved as reliefs on Pakerisan cliffs.
- Gate shaped temple with a doorway. Examples of such temple is the Plumbangan Gate, Bajang Ratu Gate, and Jedong Gate.
- Other types of Gate shaped temple which split to halved for entrance and exit. Examples of such temple is the Bentar Gate and the Wringin Lawang Gate.
Borobudur Temple

Mendut Temple

Kalasan Temple
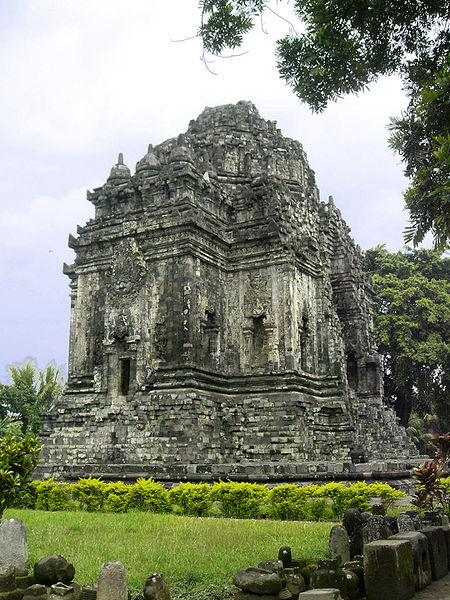

Prambanan Temple

Penataran Temple

Tikus Temple / Candi Tikus

Padas Temple in Gunung Kawi

Bajang Ratu Temple

Wringin Lawang Gate

2. Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on Fine Art
Indonesia Fine art that heavily influenced by the Hindu-Buddhist culture of India is sculpture or carving. Sculpture or carving, usually in the form of wall decorations on temple with Mahameru mountain themes, the residence of the gods. Ornaments found on the doorstep is the head of Kala ( Some kind of Giant ) called Vanaspati (king of the jungle). Kala found on temples in Central Java is always coupled with a makara, a crocodile that decorate the bottom right and left of the doors.
Other form of decoration is leaves pattern strung with tendrils curled into tendrils coil. This pattern decorate the horizontal and vertical of upper platform. There are also other forms of decoration in the form of a blue lotus (utpala), red (padam), and white (kumala). These patterns are not distinguished by lotus color, but its details differ. Especially on the temple walls in Central Java, there decoration of Kalpataru tree (a kind of fig) is flanked by two animals or a pair of walnut.
Some temples have reliefs depicting the story. The story is taken from the book of literary or religious. Style of the relief in each region is unique. The Relief in East Java is using mayang style with its objects shaped flat (two-dimensional). The relief Style in Central Java is naturalistic style with indentations in giving the impression of three dimensions. At the time of the Majapahit Empire, relief in East Java imitating Central Java by providing background scenery as to create the impression of three dimensions.
Some example of popular reliefs are as follows:
- Reliefs of Borobudur tells Kormanibhangga, it's describe human actions with laws in accordance with the Gandawyuha (Sudhana seeking knowledge).
- Roro Jonggrang Temples reliefs telling the story of Ramayana and Kresnayana.
Sculpture that are evolving generally are a sculpture of a king statue in a temple. King of the dead honored in the form of god statues. Examples of sculpture from Hindu-Buddhist culture results can we now see at the Prambanan temple ( Jonggrang statues ) and at the Museum of Mojokerto ( East Java ). One of the most beautiful collections of the museum is a statue of Airlangga (manifestation of Vishnu) and the statue of Ken Dedes.
Kala Sculpture

Makara Sculpture

Karmawibhangga Relief

Roro Jongrang Temples Relief

3. Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on literary arts
Epic or heroic stories from India that are socialized and influenced the lives of social and cultural development in Indonesia is the story of the Mahabharata and Ramayana.
Mahabharata Book consists of eighteen volumes (parwa). Each volume is divided into several sections (also called parwa) and were composed in verse. The story essentially covers 24,000 Seloka. Most of the book is told during the eight days of fierce battle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. Mahabharatayudha word itself means great battle between Bharata families. According to the story, this book was compiled by Wiyasa Dwipayana. However, historians believe that it makes more sense if the book is a collection of Brahmin stories between 400 BC to 400 AD.
Book of Ramayana was authored by Valmiki. This book consists of seven volumes (kanda) and composed in verse counting to 24,000 Seloka. This book contains the story of Rama battle for reclaiming his wife, Dewi Sinta (Sita), who was abducted by Ravana.
In his struggle, Rama whose always accompanied by Lakshmana (his little brother) was getting help from a monkey army led by Sugriva. In addition, Rama was also helped by Wibhisana Gunawan, brother of Ravana who was expelled by his brother because he intends to support the righteousness ( Rama ) . The struggle is causing major wars and many victims. At the end of the story, Ravana, along with his men killed and Sinta then returned to Rama.
Acculturation in the literature can be seen in the modification of the India original stories by inserting Indonesian elemental figures and events that make the story seemed happen in Indonesia. An example is the addition of clown figure (Semar, Bagong / Cepot, Gareng, Petruk).
In the story of the Mahabharata. In fact, in the religious literature of Hindu-Buddhist in Indonesia, it is hard to find original stories like the one in it's native country. The influence of Indian literature that are preserved is in the form of of ideas, concepts, and it's views.
Semar

Petruk, Gareng and Bagong / Cepot

4. Hindu-Buddhist cultural influence on government system
One obvious example of Hindu-Buddhist cultural influence in Indonesia is a change in the government system. Before the Hindu-Buddhist influence in Indonesia, the Indonesian native social structure shaped by tribal leaders appointed on the principle of primus inter pares ( The Most Senior Person ). After the Hindu-Buddhist influence come, the system was changed to the royal government. Leadership then passed down to descendants of the king. The king and his family then forming the so-called nobility.
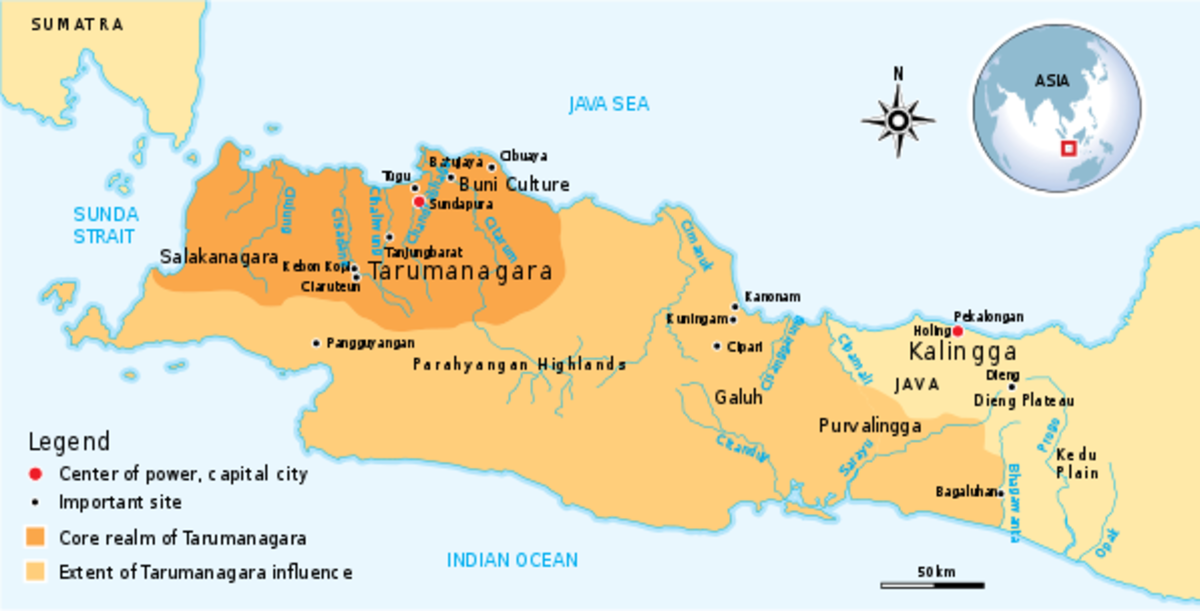
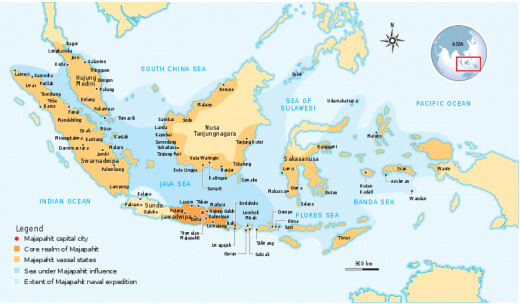
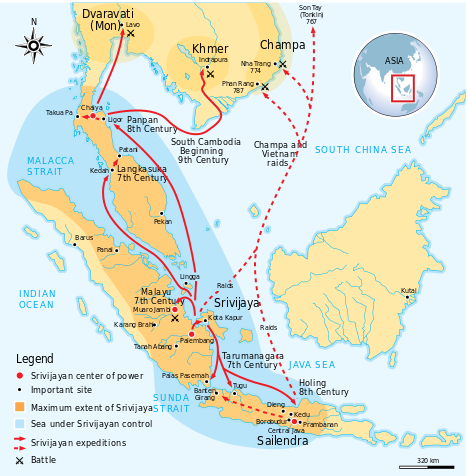
In development, there are two Type of empire based on Hindu-Buddhist culture. Hindu Style kingdoms, among others, the Kingdom of Kutai, Tarumanegara, Hindu Mataram (Mataram Ancient), Kahuripan (Airlangga) and Majapahit. Majapahit is the Largest Hindu Kingdom in Indonesia. The Buddhist styled kingdoms, among others, the Holing Kingdom (Kalinga), Malay, Srivijaya, and Mataram Buddha. Sriwijaya in the Largest Buddha Kingdom in Indonesia.
Majapahit Empire
Srivijaya Empire
5. Hindu-Buddhist cultural influences on belief systems
At the time Hindu-Buddhist culture reach Indonesia, people still adhere to the original trust, the animism and dynamism. Due to the process of acculturation, Hinduism and Buddhism then accepted by the natives. Compared to Hinduism, Buddhism more easily accepted by the general public so it developed more rapidly and spread to many different areas in Indonesia. The reason for this is that Buddhism does not recognize caste, does not discriminate against men, and assume all men are equal before God (non-discriminatory). According to Buddhism, every human being can attain nirvana provided both mind and character and contributed to society.
That's it for now
Well that's it for now. Like i said before, i'm gonna split this article into two part. This one part almost take a week to finish, and since next week i'm going on some business trip, i think it will take two weeks before the second part show up.
Feels free to leave any comment for now.
Thanks for reading